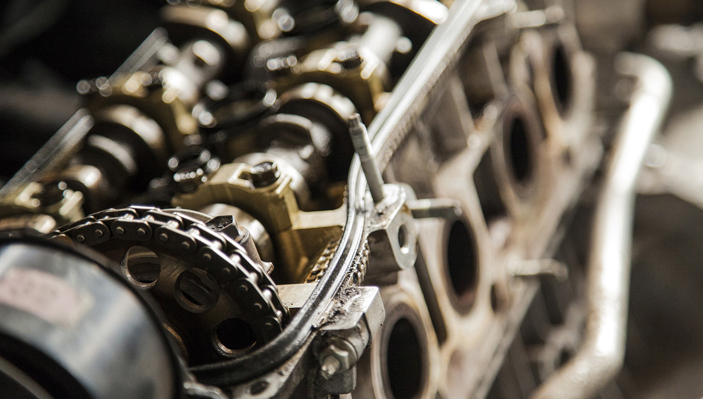
Work Environment
This occupation is typically found in the following Career Sector(s):
Videos on the Web
- Machinist - Manufacturing- from: Youtube Search
Most commonly reported Work Activities
- Controlling Machines and Processes Using either control mechanisms or direct physical activity to operate machines or processes (not including computers or vehicles).
- Getting Information Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
- Inspecting Equipment, Structures, or Material Inspecting equipment, structures, or materials to identify the cause of errors or other problems or defects.
- Monitor Processes, Materials, or Surroundings Monitoring and reviewing information from materials, events, or the environment, to detect or assess problems.
- Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events Identifying information by categorising, estimating, recognising differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events.
- Repairing and Maintaining Mechanical Equipment Servicing, repairing, adjusting, and testing machines, devices, moving parts, and equipment that operate primarily on the basis of mechanical (not electronic) principles.
- Communicating with Supervisors, Peers, or Subordinates Providing information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates by telephone, in written form, e-mail, or in person.
- Making Decisions and Solving Problems Analysing information and evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems.
- Handling and Moving Objects Using hands and arms in handling, installing, positioning, and moving materials, and manipulating things.
- Training and Teaching Others Identifying the educational needs of others, developing formal educational or training programs or classes, and teaching or instructing others.
Working Life
- Interpret engineering drawings and carry out model based inspection of components
- Support key business metrics with ongoing process improvements and introduction of new manufacturing processes and technologies.
- Support manufacturing process development to meet project milestones and to allow operations to meet their targets.
- Drive process improvements/capacity increases through new technology / equipment selection and specification.
- Validate requirements on new equipment introductions / processes / process changes.
- Design & develop tools, fixtures, and gauges for manufacturing operations and new product / process introductions in conjunction with toolroom technicians and process engineers.
- Preparation and maintenance of all relevant manufacturing specifications.
Most commonly reported Work Tasks
- Calculate dimensions or tolerances, using instruments, such as micrometers or vernier calipers.
- Machine parts to specifications, using machine tools, such as lathes, milling machines, shapers, or grinders.
- Measure, examine, or test completed units to check for defects and ensure conformance to specifications, using precision instruments, such as micrometers.
- Set up, adjust, or operate basic or specialised machine tools used to perform precision machining operations.
- Program computers or electronic instruments, such as numerically controlled machine tools.
- Study sample parts, blueprints, drawings, or engineering information to determine methods or sequences of operations needed to fabricate products.
- Monitor the feed and speed of machines during the machining process.
- Maintain machine tools in proper operational condition.
- Fit and assemble parts to make or repair machine tools.
- Align and secure holding fixtures, cutting tools, attachments, accessories, or materials onto machines.
Further Information
- CNC Machinist- from: N.C.S. [UK]
Interests - Machinist - Manufacturing
This occupation is typically suited for people with the following Career Interests:
Realist
Realists are usually interested in 'things' - such as buildings, mechanics, equipment, tools, electronics etc. Their primary focus is dealing with these - as in building, fixing, operating or designing them. Involvement in these areas leads to high manual skills, or a fine aptitude for practical design - as found in the various forms of engineering.
Realists like to find practical solutions to problems using tools, technology and skilled work. Realists usually prefer to be active in their work environment, often do most of their work alone, and enjoy taking decisive action with a minimum amount of discussion and paperwork.
Administrative
Administrative people are interested in work that offers security and a sense of being part of a larger process. They may be at their most productive under supervisors who give clear guidelines and while performing routine tasks in a methodical and reliable way.
They tend to enjoy clerical and most forms of office work, where they perform essential administrative duties. They often form the backbone of large and small organisations alike. They may enjoy being in charge of office filing systems, and using computers and other office equipment to keep things running smoothly. They usually like routine work hours and prefer comfortable indoor workplaces.
Investigative
The Investigative person will usually find a particular area of science to be of interest. They are inclined toward intellectual and analytical activities and enjoy observation and theory. They may prefer thought to action, and enjoy the challenge of solving problems with sophiscticated technology. These types prefer mentally stimulating environments and often pay close attention to developments in their chosen field.
Entry / Progression - Machinist - Manufacturing
There are many pathways to develop the skills & qualifications to progress to a precision parts & machinist career.
Sample Education and Training Pathways
A number of courses are available throughout the country that focus on learning and skills that may be useful for this career. The examples and links below may guide you in your research.
Further Education (FET)
Further Education & Training (FET) Courses are delivered by local ETBs, ranging in duration from several weeks up to 20 months. Courses are designed to meet the labour market needs and often include a large element of work experience.
Example search terms include: engineering, manufacturing operations.
Search for FET Courses
PLC Courses (FET)
PLC courses are full-time courses, one or two years duration, with awards at Level 5 and 6 on the NFQ. They are offered nationally in Schools and Colleges of Further Education.
Example search terms include: engineering, pre-apprenticeship.
Search for PLC Courses
Apprenticeships:
Apprenticeships are structured work-based training programs that combine on-the-job training with classroom instruction. They run from 2 – 4 years and are open to individuals of all ages, including school leavers, those seeking a career change, and existing employees who wish to upskill.
Examples: Metal Fabrication, Precision Machinist and Quality Control, Precision Turned Parts Manufacturing.
Search for Apprenticeships
- To become an apprentice in Ireland you must be hired by an employer.
- Apprenticeship employers are formally approved by SOLAS in advance of employing apprentices. Apprentices get a formal contract of employment as part of their apprenticeship.
To find an apprenticeship, you can search apprenticeship vacancies on the Apprenticeship Jobs Portal. You can search for vacancies by location and by apprenticeship.
Higher Education CAO (Undergraduate)
Higher Education courses at Levels 6 to 8 on the NFQ, delivered in Universities and Technological Universities & Institutes. Courses run from 2 – 5 years and places are allocated on a points-based system, processed by the Central Application Office.
Example search terms include: precision engineering, design.
Search for CAO Courses
Pay & Salary - Machinist - Manufacturing
Salary Range (thousands per year)* €26k - €55k
Salaries vary by employer, location, duties, role, experience, and sessional shift pattern & conditions.
Data Source(s):
Payscale/ Indeed / Morgan McKinley/ Excel/ Clark/ Osborne
Last Updated: March, 2024
Labour Market Updates - Machinist - Manufacturing
Note: The following information relates to occupations that include: Paper and wood machine operatives; Coal mine operatives; Quarry workers and related operatives; Energy plant operatives; Metal working machine operatives; Water and sewerage plant operatives; Printing machine assistants; Plant and machine operatives n.e.c.
This information has been derived from the Solas National Skills Bulletin (2023).
Despite the strong employment growth rate for this occupation over the five-year period, employment only returned to pre-COVID-19 levels in 2022.
Although the green transition may result in an increased demand for elementary workers in energy and sewerage plant operations, the small numbers employed across the various roles in this occupation do not allow for detailed demand analysis.
Useful Contacts - Machinist - Manufacturing
-
Engineers Ireland
- 22 Clyde Road, Ballsbridge Dublin 4
- (01) 665 1300
- Click Here
-
Smart Futures
- Discover Science & Engineering, Wilton Park House, Wilton Place, Dublin, 2
-
- Click Here