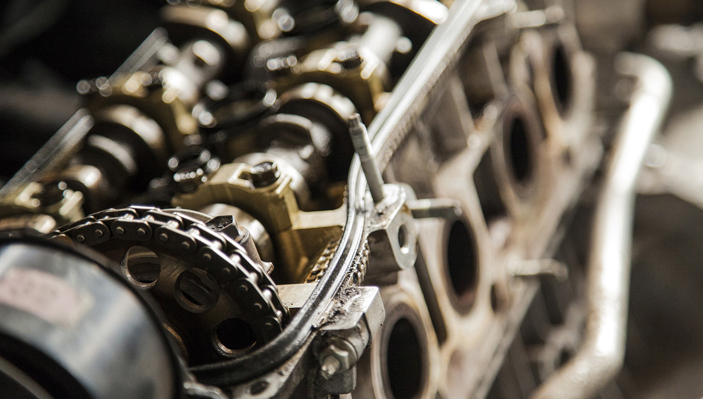
Work Environment
This occupation is typically found in the following Career Sector(s):
Videos on the Web
- Auto Electrician- from: Youtube Search
Most commonly reported Work Activities
- Getting Information Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
- Making Decisions and Solving Problems Analysing information and evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems.
- Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events Identifying information by categorising, estimating, recognising differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events.
- Updating and Using Relevant Knowledge Keeping up-to-date technically and applying new knowledge to your job.
- Handling and Moving Objects Using hands and arms in handling, installing, positioning, and moving materials, and manipulating things.
- Interacting With Computers Using computers and computer systems (including hardware and software) to program, write software, set up functions, enter data, or process information.
- Operating Vehicles, Mechanised Devices, or Equipment Running, maneuvering, navigating, or driving vehicles or mechanised equipment, such as forklifts, passenger vehicles, aircraft, or water craft.
- Processing Information Compiling, coding, categorising, calculating, tabulating, auditing, or verifying information or data.
- Thinking Creatively Developing, designing, or creating new applications, ideas, relationships, systems, or products, including artistic contributions.
- Organising, Planning, and Prioritising Work Developing specific goals and plans to prioritise, organise, and accomplish your work.
Working Life
They use ammeters and voltmeters to identify breaks in electric circuits. They check electronic circuits against circuit diagrams and use hand and power tools to make repairs. When a repair is completed, they test the circuit or part to make sure it is working correctly. They also make adjustments, and check and top up batteries as part of routine servicing. They may take part in MOT tests, to make sure a vehicle is safe to travel on the road.
Auto-electricians may install and repair accessories such as audio systems, alarms, car phones DVD and TV, Satellite Navigation. They may go to breakdowns with mechanics and repair faults at the site.
Auto-electricians may specialise in cars, heavy goods vehicles, buses or coaches. They may specialise in one make of vehicle.
Most auto-electricians work is in garages, workshops or depots that are large, airy spaces with concrete floors, and are cold in winter and hot in summer. They wear overalls or boiler suits and rub their hands with barrier cream to protect them against oil, grease and dirt. Much of the time auto-electricians are under a vehicle or its dashboard, testing or repairing. They deal with all aspects of the car from starter motor, to central locking, to electric windows.
Most commonly reported Work Tasks
- Install equipment and accessories, such as stereos, navigation equipment, communication equipment, and security systems.
- Inspect and test electrical or electronic systems to locate and diagnose malfunctions, using visual inspections and testing instruments, such as oscilloscopes and voltmeters.
- Cut openings and drill holes for fixtures and equipment, using electric drills and routers.
- Splice wires with knives or cutting pliers, and solder connections to fixtures and equipment.
- Diagnose or repair problems with electronic equipment, such as sound, navigation, communication, and security equipment, in motor vehicles.
- Run new speaker and electrical cables.
- Confer with customers to determine the nature of malfunctions.
- Remove seats, carpeting, and interiors of doors and add sound-absorbing material in empty spaces, reinstalling interior parts.
- Record results of diagnostic tests.
- Estimate costs of repairs, based on parts and labor charges.
Qualities - Auto Electrician
To be an auto-electrician, you need a logical and methodical mind to trace faults. Auto-electricians must be good with their hands, and physically fit to cope with lifting, bending and working in cramped conditions, for example, stretching under a dashboard.
You must be able to work accurately on your own, and as part of a team. You need to be able to make decisions and take responsibility for your work, which can affect the safety of customers and colleagues. Auto-electricians must have good communication skills to discuss faults with drivers and colleagues. You must be able to understand written instructions, and perhaps technical drawings. You should have good problem skills. You would also need to keep up to date with developments in technology.
Good colour vision is needed for working with colour coded wires and parts.
Interests - Auto Electrician
This occupation is typically suited for people with the following Career Interests:
Realist
Realists are usually interested in 'things' - such as buildings, mechanics, equipment, tools, electronics etc. Their primary focus is dealing with these - as in building, fixing, operating or designing them. Involvement in these areas leads to high manual skills, or a fine aptitude for practical design - as found in the various forms of engineering.
Realists like to find practical solutions to problems using tools, technology and skilled work. Realists usually prefer to be active in their work environment, often do most of their work alone, and enjoy taking decisive action with a minimum amount of discussion and paperwork.
Investigative
The Investigative person will usually find a particular area of science to be of interest. They are inclined toward intellectual and analytical activities and enjoy observation and theory. They may prefer thought to action, and enjoy the challenge of solving problems with sophiscticated technology. These types prefer mentally stimulating environments and often pay close attention to developments in their chosen field.
Administrative
Administrative people are interested in work that offers security and a sense of being part of a larger process. They may be at their most productive under supervisors who give clear guidelines and while performing routine tasks in a methodical and reliable way.
They tend to enjoy clerical and most forms of office work, where they perform essential administrative duties. They often form the backbone of large and small organisations alike. They may enjoy being in charge of office filing systems, and using computers and other office equipment to keep things running smoothly. They usually like routine work hours and prefer comfortable indoor workplaces.
Entry / Progression - Auto Electrician
There are many pathways to develop skills & qualifications towards a career as a Mechanic automotive technician.
ETBs Education training boards via skills to advance offer part time upskilling in electrical automotive diagnostics NFQ component awards level 5 Auto Electricity search our FET centre CourseFinder
The official entry route for a Mechanic is by undertaking an apprenticeship NFQ level 6.

The minimum entry requirement is at that you are at least 16 years old and have at least a grade D in any 5 subjects in the Junior Certificate (or equivalent grades in other approved examinations). Some employers will look for more than this – up to Leaving Certificate.
You also need to pass a colour vision test approved by SOLAS.
Math, physics, technical drawing, metal work, technology and engineering are particularly relevant school subjects.
To work as a mechanic, you will also be expected to have a Full Drivers Licence.
Sample Education and Training Pathways
A number of courses are available throughout the country that focus on learning and skills that may be useful for this career. The examples and links below may guide you in your research.
Further Education (FET)
Further Education & Training (FET) Courses are delivered by local ETBs, ranging in duration from several weeks up to 20 months. Courses are designed to meet the labour market needs and often include a large element of work experience.
Example search terms include: motor vehicle maintenance, automotive technology.
Search for FET Courses
PLC Courses (FET)
PLC courses are full-time courses, one or two years duration, with awards at Level 5 and 6 on the NFQ. They are offered nationally in Schools and Colleges of Further Education.
Example search terms include: motor vehicle maintenance, automotive technology.
Search for PLC Courses
Apprenticeships:
Apprenticeships are structured work-based training programs that combine on-the-job training with classroom instruction. They run from 2 – 4 years and are open to individuals of all ages, including school leavers, those seeking a career change, and existing employees who wish to upskill.
Examples: Motor Mechanic, Heavy Vehicle Mechanic
Search for Apprenticeships
Higher Education CAO (Undergraduate)
Higher Education courses at Levels 6 to 8 on the NFQ, delivered in Universities and Technological Universities & Institutes. Courses run from 2 – 5 years and places are allocated on a points-based system, processed by the Central Application Office.
Example search terms include: management, electrical, vehicle, automotive, engineering.
Search for CAO Courses
Springboard offer blended programs in Electrical Automotive Technology NFQ level 7.
As a qualified mechanic, you can work in a number of settings, the most common one being in a garage or car sales business. With experience and significant funds, you can start your own garage or you can progress by specialising, in a particular brand of a car or a specific type of vehicle (e.g. electric and hybrid) or in tuning and modifying vehicles for higher performance, for example.
As a qualified motor mechanic, you can also work as an NCT Inspector in an NCTS (National Car Testing Services). Whilst a completed mechanic qualification (i.e. apprenticeship) is required to get the job, you will receive comprehensive induction training for 3 weeks to qualify you to perform the NCT tests. You will also be required to participate in annual refresher training on the NCT testing procedures and use of the equipment. Occupational First Aid and Health and Safety training is also provided by the employer on a regular basis for employees.
As a qualified Heavy Goods Vehicle Mechanic, you can work in a CVRT (Commercial Vehicle Roadworthiness Test) Centre and training is provided to successful applicants to become a CVRT tester.
As the motor industry develop with technological advancements all the time, it is important to keep up to date. Industry organisations, such as the Society of the Irish Motor Industry, often offer training opportunities to mechanics and other professionals in the sector via Skillsnets network.
Pay & Salary - Auto Electrician
Salary Range (thousands per year)* €18k - €50k
Salaries vary depending on employer, location, experience, and duties. Apprentices rates develop based on phase entry points till qualified rates.
Data Source(s):
Payscale/ Salary expert / Glassdoor/ Talent/ Indeed
Last Updated: March, 2024
Labour Market Updates - Auto Electrician
Note: The following information relates to occupations that include: Vehicle technicians; Vehicle mechanics and electricians; Vehicle body builders and repairers; Vehicle paint technicians; Aircraft maintenance and related trades; Boat and ship builders and repairers; Rail and rolling stock builders and repairers.
This information has been derived from the Solas National Skills Bulletin (2023).
Employment levels have seen little change in recent years resulting in a below average annual growth rate over the five-year period. Census data shows that although employment is spread across a range of roles, the majority are employed as vehicle technicians, mechanics and electricians.
There was a higher-than-average share of non-Irish citizens employed (25% compared to 19% nationally). Employment permits issued for this occupation were mainly for vehicle roadworthiness testers with a small number for aircraft engineers. Vacancies advertised through DSP Jobs Ireland included various mechanics (aircraft, HGV, motor) and vehicle inspectors. There was a relatively high volume of jobseekers registered with the DSP in December 2022 who had previously been employed in vehicle trades roles.
New apprenticeship registration numbers for both HGV and motor mechanics declined in 2022 when compared to the previous year but were relatively on a par with 2019 levels. The decline in new diesel and petrol car registrations along with the increased uptake of electric and hybrid vehicles is likely to result in an increased demand for electric vehicle (EV) mechanics and a gradual decline in demand for traditional motor mechanic skills.
In 2022, there were 15,462 EV cars licensed for the first time in Ireland, representing a 3.5-fold increase (+349%) on 2019 numbers. Growth is expected to continue, as in the first five months of 2023 numbers had already reached nearly 12,000, a 52% increase on the same period in the preceding year. Although no shortages have been identified, upskilling/reskilling in digital skills will be required for the current vehicle mechanic workforce.
Useful Contacts - Auto Electrician
-
Society of the Irish Motor Industry